-
Mobile Version
Scan with Mobile
- Member Center
 682
682
Scaffolding, also called scaffold or staging, is a temporary structure used to support a work crew and materials to aid in the construction, maintenance and repair of buildings, bridges and all other human-made structures. Scaffolds are widely used on site to get access to heights and areas that would be otherwise hard to get to. Unsafe scaffolding has the potential to result in death or serious injury. Scaffolding is also used in adapted forms for formwork and shoring, grandstand seating, concert stages, access/viewing towers, exhibition stands, ski ramps, half pipes and art projects.
There are six main types of scaffolding used worldwide today. These are tube and coupler (fitting) components, prefabricated modular system scaffold components, H-frame / façade modular system scaffolds, suspended scaffolds, timber scaffolds and bamboo scaffolds (particularly in China, India and Hong Kong). Each type is made from several components which often include:
A base jack or plate which is a load-bearing base for the scaffold.
The standard, the upright component with connector joins.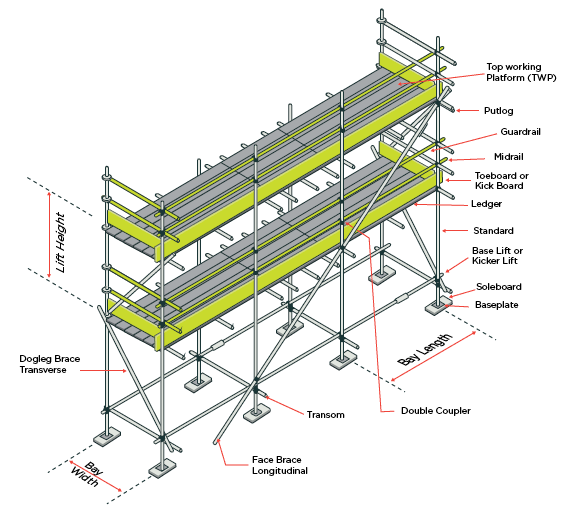
The ledger, a horizontal brace.
The transom, a horizontal cross-section load-bearing component which holds the batten, board, or decking unit.
Brace diagonal and/or cross section bracing component.
Batten or board decking component used to make the working platform.
Coupler, a fitting used to join components together.
Scaffold tie, used to tie in the scaffold to structures.
Brackets, used to extend the width of working platforms.
Specialized components used to aid in their use as a temporary structure often include heavy duty load bearing transoms, ladders or stairway units for the ingress and egress of the scaffold, beams ladder/unit types used to span obstacles and rubbish chutes used to remove unwanted materials from the scaffold or construction project.

